Learning Outcomes:
i. Understand the concept of sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds in ethene.
ii. Analyze how sigma and pi bonds contribute to the trigonal planar shape of the ethene molecule.
iii. Visualize the three-dimensional structure of ethene and its implications for its properties.
iv. Recognize the significance of understanding bond types and molecular geometry in organic chemistry.
Introduction:
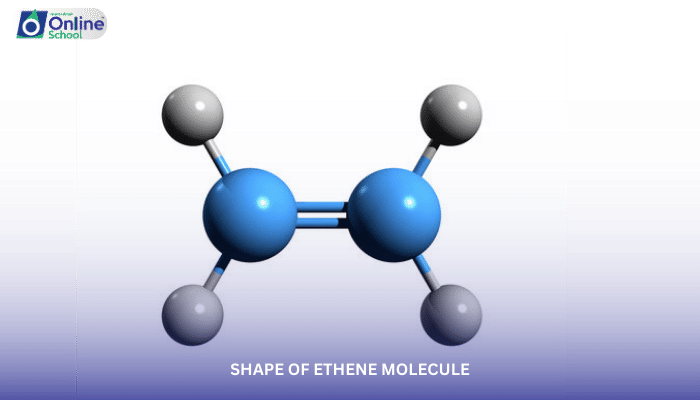
Ethene, commonly known as ethylene, is the simplest alkene, containing one double bond between two carbon atoms. Delving into the realm of ethene's molecular structure, this lesson explores the interplay of sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds in shaping the ethene molecule, laying a foundation for comprehending the three-dimensional geometry of organic compounds.
i. Sigma (σ) Bond: The Foundation of Covalent Bonding
Sigma bonds, formed by the head-on overlap of hybridized orbitals, are the strongest and most prevalent type of covalent bond. In ethene, the two carbon atoms involved in the double bond form a sigma bond by overlapping their sp2 hybridized orbitals.
ii. Pi (π) Bond: Expanding the Bonding Landscape
Pi bonds, arising from the sideways overlap of unhybridized p orbitals, are weaker than sigma bonds but crucial for forming multiple bonds. In ethene, each carbon atom contributes one unhybridized p orbital, forming a pi bond perpendicular to the sigma bond.
iii. Trigonal Planar Shape: A Consequence of Bonding
The sigma bond restricts rotation around the carbon-carbon axis, while the pi bond permits rotation, albeit with a high energy barrier. This restricted rotation, along with the sp2 hybridization of carbon atoms, results in the trigonal planar shape of ethene.
iv. Three-Dimensional Structure: Visualization and Implications
The trigonal planar shape of ethene has significant implications for its properties and reactivity. The molecule's flat structure and lack of steric hindrance make it highly reactive and prone to addition reactions.
v. Significance of Bond Types and Molecular Geometry
Understanding the concepts of sigma and pi bonds and their influence on molecular geometry is fundamental in organic chemistry. It provides insights into the three-dimensional structure of molecules, their physical properties, and their chemical reactivity.
The shape of the ethene molecule, determined by the interplay of sigma and pi bonds, epitomizes the fascinating interplay of bonding and molecular geometry in organic chemistry. By comprehending these concepts, students gain a deeper understanding of the structure and properties of organic compounds, paving the way for further exploration in this intricate field.